Ever wondered if there’s a way to unlock the value of your assets without selling them off? Or perhaps, a means to diversify your investment portfolio with stable returns? The answer lies in the realm of Asset Backed Securities in India. (ABS).
Think of it this way: You own a number of properties generating regular income. What if you could convert this future cash flow into a tradable, marketable security? Welcome to the world of ABS, financial instruments backed by a pool of assets.
But what types of asset backed securities in India exist? Are asset backed securities derivatives? How does asset backed securities pricing work? And, importantly, how can these be harnessed in India?
As we delve into this fascinating domain, we’ll uncover ABS’s mechanics, benefits, and possibilities, offering a fresh perspective on asset protection and value maximisation. Fasten your seatbelts, and let’s embark on this financial exploration!

What is Asset Backed Security?
ABS provides issuers with a means to raise capital by pooling illiquid assets and transforming them into marketable financial instruments through securitisation.
This process not only enhances liquidity but also mitigates credit risk by transferring shakier assets off the issuer’s books.
ABS can be structured using various underlying assets, from home equity and automobile loans to credit card receivables, student loans, and even unconventional revenue streams like movie royalties or solar photovoltaics.
This flexibility allows investors to access diverse income-generating assets that may be unavailable through other investment avenues.
By investing in Asset backed securities in India, individuals and institutions can tap into unique revenue streams and potentially benefit from the stability and returns offered by these carefully structured financial instruments.
How Does Asset-Backed Security Work
Let’s assume company X, specialising in automobile loans, may encounter a situation where it requires additional funds to continue lending.
To address this, Company X can bundle its existing loans and sell them to Investment Firm X. This transaction provides Company X with immediate cash, which can be used to extend new loans.
Upon acquiring the loans, Investment Firm X organises them into distinct groups known as tranches. Each tranche consists of loans sharing common characteristics like maturity, interest rate, and projected delinquency rate.
Investment Firm X then issues securities based on each tranche, akin to bonds, with each asset-backed security (ABS) being assigned a rating that reflects the level of risk associated with the underlying loans.
Individual investors have the opportunity to purchase these securities, and in return, they receive the cash flows generated by the pool of auto loans. Investment Firm X retains an administrative fee for its services.
This arrangement allows investors to participate in the income generated by the loans while Investment Firm X manages the administration and distribution process.
Different Types of Asset Backed Securities
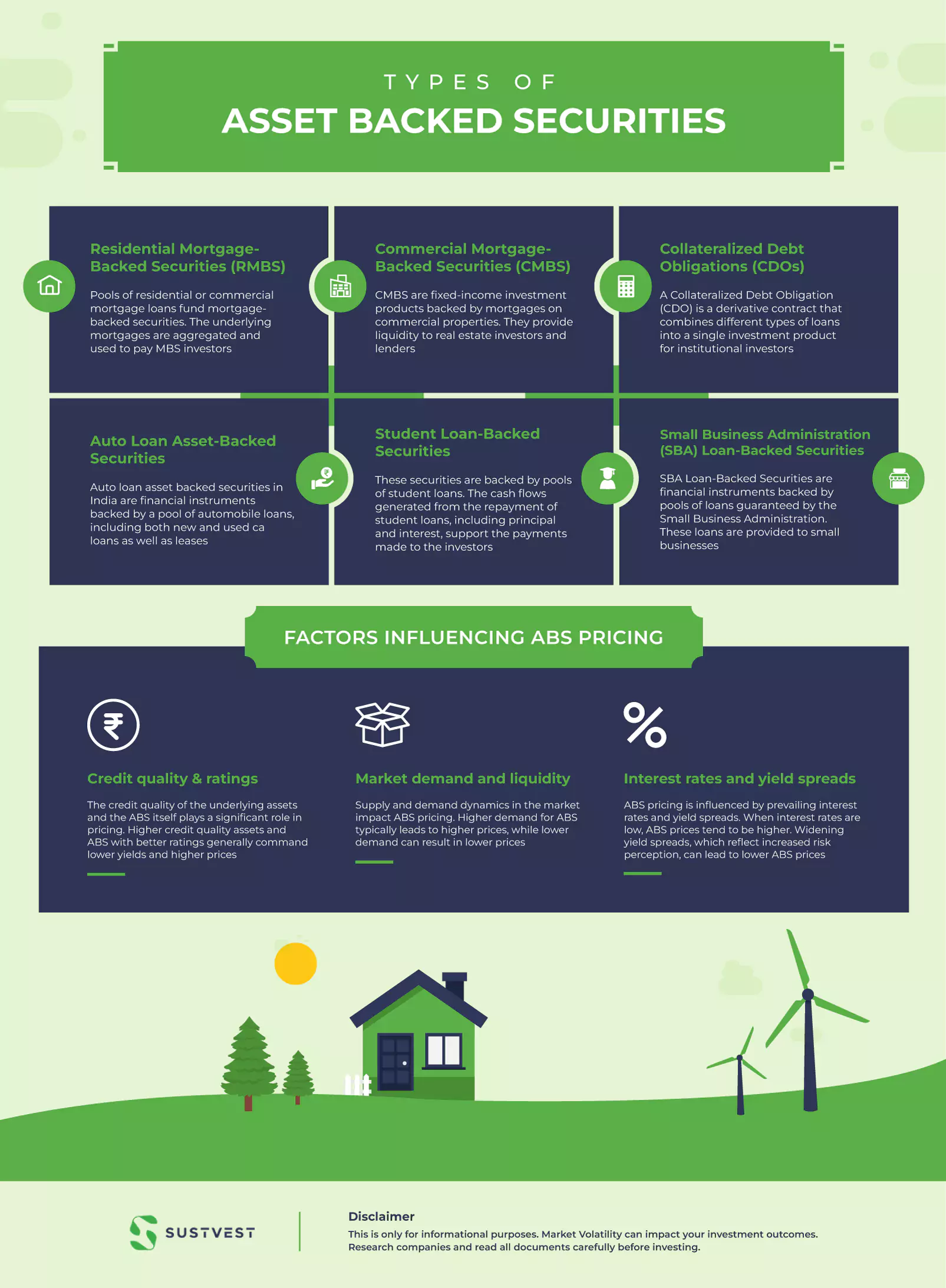
These assets may include loans, receivables, or other cash-flow assets. Types of Asset backed securities in India include:
1. Residential Mortgage-Backed Securities (RMBS)
Pools of residential or commercial mortgage loans fund mortgage-backed securities. The underlying mortgages are aggregated and used to pay MBS investors.
RMBS and CMBS are backed by residential and commercial mortgages, respectively. Investors in MBS receive payments based on borrowers’ mortgage loan interest and principal payments.
2. Commercial Mortgage-Backed Securities (CMBS)
CMBS are fixed-income investment products backed by mortgages on commercial properties. They provide liquidity to real estate investors and lenders.
CMBS lacks standardised structures, making its valuation challenging. These securities include various commercial mortgages with different terms, values, and property types like multi-family dwellings and commercial real estate.
Unlike residential mortgage-backed securities (RMBS), CMBS typically have less pre-payment risk due to fixed terms on commercial mortgages.
3. Collateralized Debt Obligations (CDOs)
A Collateralized Debt Obligation (CDO) is a derivative contract that combines different types of loans into a single investment product for institutional investors.
It uses underlying assets as collateral, and if a loan defaults, those assets become collateral for the CDO holders.
The CDO holder collects the borrowed amount from the original borrower, theoretically at the end of the CDO’s tenure, since the CDO comprises various loans.
4. Auto Loan Asset-Backed Securities
Auto loan asset backed securities in India are financial instruments backed by a pool of automobile loans, including both new and used car loans as well as leases.
These securities allow investors to invest in the vehicle loan market, with credit risk based on borrowers’ creditworthiness.
5. Student Loan-Backed Securities
These securities are backed by pools of student loans. The cash flows generated from the repayment of student loans, including principal and interest, support the payments made to the investors.
6. Small Business Administration (SBA) Loan-Backed Securities
SBA Loan-Backed Securities are financial instruments backed by pools of loans guaranteed by the Small Business Administration. These loans are provided to small businesses.
The cash flows generated from loan repayments made by the borrowers support the payments made to the investors of these securities.
By securitising these loans, investors have the opportunity to invest in a diversified pool of small business loans, while the SBA guarantee provides an added layer of credit enhancement.
Asset Backed Securities in India : Derivatives or Not?
Financial derivatives are based on an underlying asset or collection of assets. Hedging, speculating, and arbitrage can be done with them.
Asset backed securities in India are backed by mortgages, vehicle loans, or credit card receivables. ABS holders receive payments based on the cash flows generated by these underlying assets.
While ABS and derivatives share some similarities, such as their complexity and the use of underlying assets, there are fundamental differences between the two.
ABS represents ownership in the underlying assets, whereas derivatives represent a contractual right or obligation tied to the assets. ABS provides direct exposure to the cash flows from the assets, while derivatives offer indirect exposure through contracts.
Given these distinctions, ABS should not be classified as derivatives. ABS holders have direct ownership and are entitled to the cash flows generated by the underlying assets, unlike derivative holders, who have contractual rights tied to the assets’ value.
Factors Influencing ABS Pricing
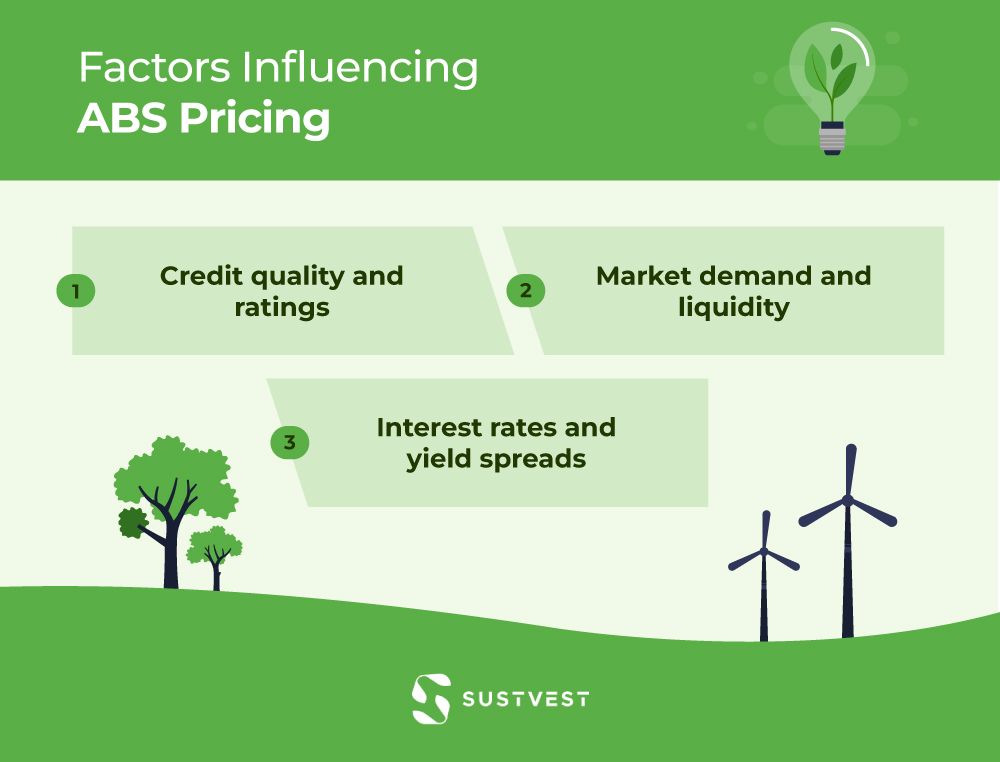
Factors influencing asset backed securities in India pricing include:
- Credit quality and ratings: The credit quality of the underlying assets and the ABS itself plays a significant role in pricing. Higher credit quality assets and ABS with better ratings generally command lower yields and higher prices.
- Market demand and liquidity: Supply and demand dynamics in the market impact ABS pricing. Higher demand for ABS typically leads to higher prices, while lower demand can result in lower prices. Liquidity in the market also affects pricing, with more liquid ABS generally having tighter spreads and higher prices.
- Interest rates and yield spreads: ABS pricing is influenced by prevailing interest rates and yield spreads. When interest rates are low, ABS prices tend to be higher. Widening yield spreads, which reflect increased risk perception, can lead to lower ABS prices.
Credit enhancements are mechanisms designed to mitigate credit risk and enhance the credit quality of ABS. These enhancements can include over-collateralization, cash reserves, and third-party guarantees.
The presence of credit enhancements improves investor confidence and reduces perceived risk, resulting in higher price of asset backed securities in India and lower yields.
Pricing Methodologies And Valuation Techniques
There are various pricing methodologies and valuation techniques used for ABS. These can include discounted cash flow analysis, option-adjusted spread models, and Monte Carlo simulations.
These methods consider factors such as cash flow projections, prepayment and default risk, interest rates, and market conditions to determine the fair value of ABS. Market participants may also consider observed market prices and liquidity in valuing ABS.
FAQs
How does Asset Backed Security differ from traditional bonds?
Asset supported Securities are supported by the cash flows from the underlying assets, unlike regular bonds, which are backed by the issuer. ABS is only as good as its underlying assets.
Are Asset Backed Securities considered risky investments?
The risk associated with Asset Backed Securities varies depending on the underlying assets. While some ABS, like mortgage-backed securities, was heavily affected during the 2008 financial crisis, other types, such as ABS backed by prime auto loans, have shown more resilience. It is essential to assess the credit quality and performance of the underlying assets before investing in ABS.
Can individual investors invest in Asset Backed Securities in India?
Yes, individual investors can invest in Asset Backed Securities in India. ABS are available in various forms, including publicly traded securities and private placements. However, it is important to understand the risks and conduct thorough due diligence before investing, as ABS may have specific requirements and complexities.
Conclusion
Understanding asset backed securities in India is crucial for individuals seeking to safeguard their assets. ABS serves as a means to diversify risk and provide an avenue for financial institutions to securitize loan portfolios. By pooling together various assets such as loans or receivables, ABS creates investment opportunities backed by these assets. To protect your assets, it is essential to thoroughly research and assess the underlying assets, the structure of the ABS, and the creditworthiness of the issuer. For individuals interested in sustainable investing, SustVest offers a platform where you can explore ABS options aligned with environmentally and socially responsible investments. Take proactive steps to protect your assets by staying informed and leveraging platforms like SustVest to make responsible investment choices.

Founder of Sustvest
Hardik completed his B.Tech from BITS Pilani. Keeping the current global scenario, the growth of renewable energy in mind, and people looking for investment opportunities in mind he founded SustVest ( formerly, Solar Grid X ) in 2018. This venture led him to achieve the ‘Emerging Fintech Talent of the Year in MENA region ‘ in October 2019.




