Real estate has long been recognised as a valuable asset class for diversifying investment portfolios. Two attractive real estate investing possibilities are Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) and Fractional Ownership. While both provide opportunities to invest in real estate, they differ significantly in structure, control, and potential returns. Understanding the differences between REIT vs fractional ownership is crucial for investors seeking to make informed decisions.
This article will help you decide whether a REIT or fractional ownership is best for your financial goals and preferences. So, let’s know everything about reit vs fractional ownership.

What are Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
What is REIT? simply put, REITs let investors buy real estate without owning it. They are companies that own, operate, or finance income-generating properties like commercial buildings, residential complexes, or infrastructure projects.
REITs offer investors the opportunity to participate in real estate markets with relatively low investment amounts. The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) establishes the minimum investment in REIT India. This amount differs from REIT to REIT.
By pooling funds from multiple investors, REITs provide the potential for diversification, regular income distributions, and the chance to benefit from property value appreciation.
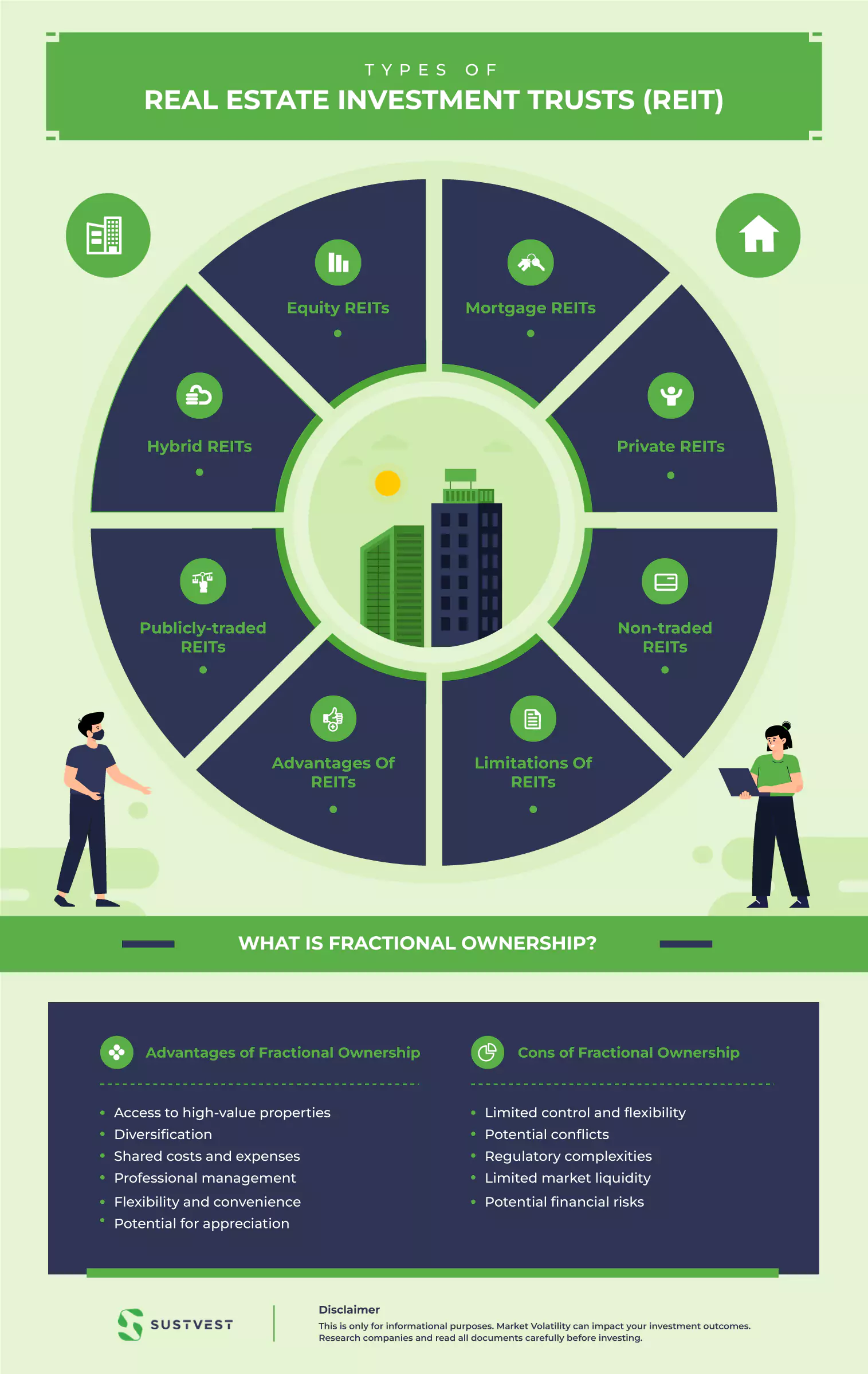
Types of Real Estate Investment Trusts (REIT)
REITs can be classified based on the types of businesses they are involved with and the methods used for buying and selling shares.
Equity REITs
This type of REIT focuses on owning and operating income-generating commercial properties. They primarily generate income through rental payments from tenants.
Understanding Equity REITs, which focus on owning and operating income-generating commercial properties, is a fascinating aspect of real estate investment.
For those interested in this area, our Guide to Equity REIT Investment in India offers a more in-depth exploration of the subject, seamlessly integrating with the ongoing journey of investment education.
Mortgage REITs
mREITs lend money to real estate owners and mortgage-backed securities traders. They make money from the interest that the loans and stocks bring in.
Hybrid REITs
Hybrid REITs mix equity and mortgage REITs. They diversify their portfolios by investing in both income-generating properties and mortgage loans, earning income from both rent and interest.
Private REITs
Private REITs are not traded on national securities exchanges and cater to a select list of investors. They are private placements and not registered with regulatory bodies like SEBI.
Publicly-traded REITs
These REITs are regulated by SEBI and offer shares on national securities exchanges. Publicly traded REITs can be bought and sold by individual investors on the exchange.
Non-traded REITs
SEBI-registered non-traded REITs are not listed on national stock markets. They are more stable than publicly traded REITs since they are less liquid and not market-sensitive.
Advantages of REITs
There are several advantages of investing in REITs:
- Diversification: REITs give investors exposure to a broad selection of real estate assets. This diversity helps to mitigate risk as investments are spread across various properties and sectors.
- Steady Income: REITs can offer a constant flow of passive income via rental payments and dividends.
- Liquidity: Publicly traded REITs can be swiftly converted into cash on stock exchanges.
- Professional Management: REITs are administered by seasoned experts who handle property procurement, management, and upkeep, freeing investors from the duties associated with direct real estate ownership.
- Accessibility: Small investors have the ability to purchase shares in publicly traded REITs for a fraction of the cost of buying individual properties, thus allowing them to invest in real estate.
Limitations of REITs
While REITs can offer attractive investment opportunities, they also have some limitations to consider:
- Absence of Tax Benefits: REITs do not provide tax advantages. Dividends from REITs are typically taxed at regular income tax rates.
- Market Risks: Like other publicly traded securities, REITs are vulnerable to market risks. Economic conditions, interest rates, and property market trends can influence the performance of REITs.
- Limited Growth Potential: REITs might have restricted growth potential compared to other investments. The income generated by REITs is primarily based on rental income, which might not keep pace with the growth rate of high-growth sectors or individual real estate investments.
While these limitations of REITs may seem daunting, a comprehensive understanding of all aspects of REITs, including their pros, cons, and investment potential, can equip you with the knowledge to navigate these challenges.
To gain a deeper insight, consider exploring our Complete Guide of REITs to Invest in India: Pros, Cons, and Investment Potential, a resource that complements this discussion, offering a broader perspective on REIT investments in India.
What is Fractional Ownership?
Fractional ownership definition – Fractional real estate investment refers to a concept where multiple investors collectively own a share or fraction of a property. Investors can buy a section of a property and use it for a year instead of buying the whole thing.
This arrangement allows investors to enjoy the benefits of property ownership, such as potential appreciation and rental income, without the need for full ownership.
Fractional ownership is often used for vacation properties or high-value assets that may be costly for individual ownership. This was all about Fractional ownership meaning.
Advantages of Fractional Ownership
Fractional ownership offers several advantages to investors:
- Access to high-value properties: Fractional ownership of property lets investors own high-value assets that would otherwise be unaffordable or unfeasible.
- Diversification: By investing in fractional ownership, individuals can diversify their real estate portfolio across different properties and locations, spreading their risk and potentially increasing their investment returns.
- Shared costs and expenses: Investors in fractional ownership share the costs and expenses associated with the property, including maintenance, repairs, and property management fees. This helps reduce the financial burden and workload on individual investors.
- Professional management: Fractional ownership often involves professional property management, ensuring that the property is well-maintained, rented out when not in use, and generating income for the investors.
- Flexibility and convenience: Fractional ownership allows investors to enjoy the benefits of property ownership, such as personal use and potential rental income, without the responsibilities and hassles associated with sole ownership. Investors can also have the flexibility to exchange their usage rights with other owners within the fractional ownership arrangement.
- Potential for appreciation: Fractional ownership offers the potential for property appreciation over time, allowing investors to benefit from any increase in property value.
Cons of Fractional Ownership
When considering fractional ownership in real estate, there are a few potential drawbacks to be aware of, particularly in the context of India:
- Limited control and flexibility: As fractional ownership involves shared ownership with other investors, decisions regarding the property, such as management, maintenance, or use, may require consensus among the owners. This can limit individual control and flexibility over the property.
- Potential conflicts: Shared ownership can cause disputes, especially if co-owners disagree on how to utilise, maintain, or rent the property. Resolving disagreements and making group decisions takes time.
- Regulatory complexities: In some jurisdictions, including India, the legal and regulatory framework around fractional ownership in real estate may be less developed or complex. It’s crucial to thoroughly understand the legal implications, rights, and responsibilities associated with fractional ownership real estate India.
- Limited market liquidity: Fractional ownership interests in real estate can have limited liquidity in the market. It can be challenging to sell or transfer fractional shares. It happens especially in regions with a less established market for such transactions, potentially limiting exit options for investors.
- Potential financial risks: Real estate investments are subject to market fluctuations and economic uncertainties. Fractional ownership does not necessarily mitigate these risks, and investors may still be exposed to potential financial losses.
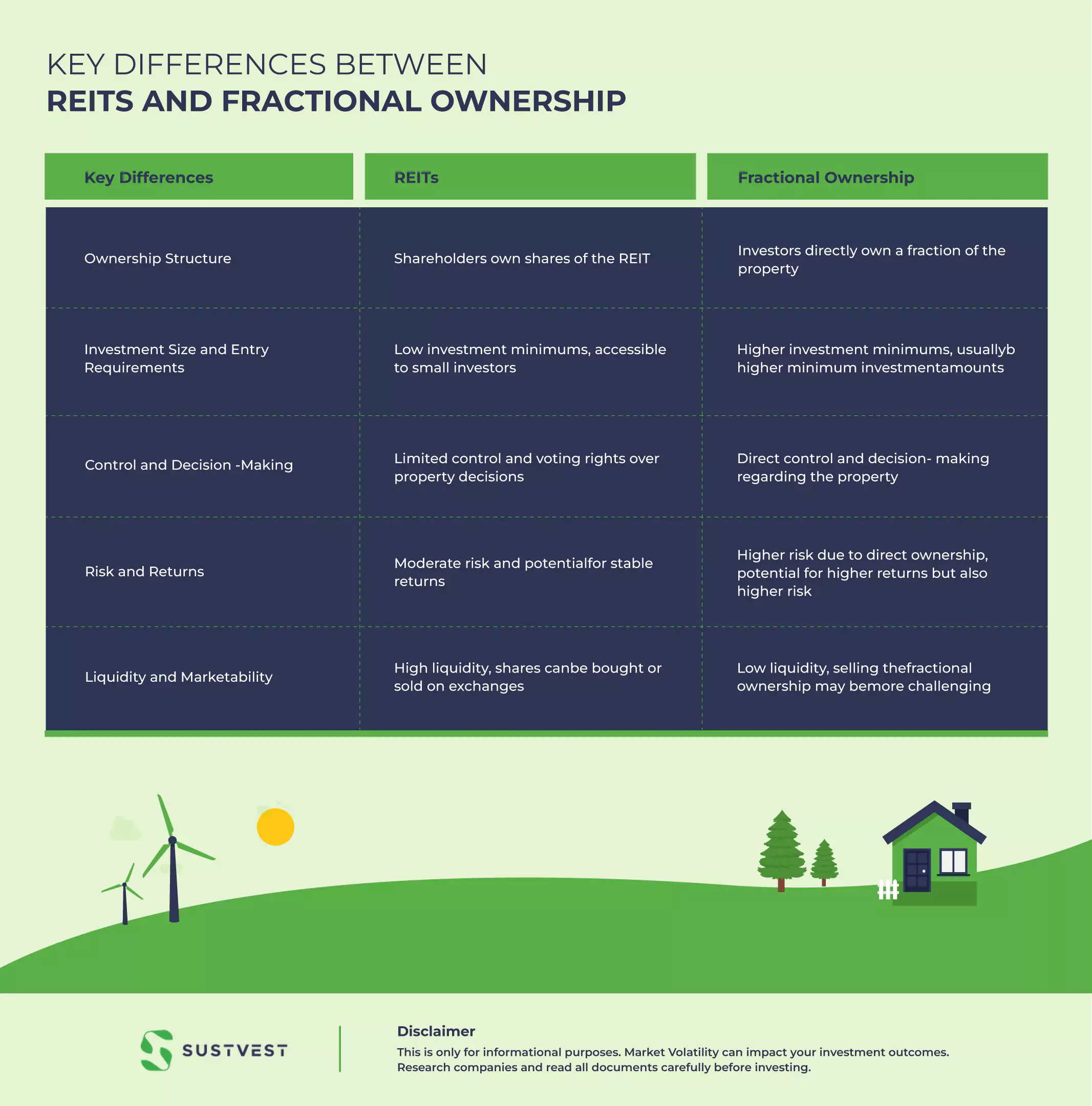
Key Differences between REIT vs Fractional Ownership
REITs are publicly traded investment vehicles that offer the diversification, professional management, and liquidity, while fractional ownership involves direct ownership of a portion of a property.
REITs provide access to a portfolio of properties, while fractional ownership allows control over specific properties. REITs have lower entry requirements and higher liquidity, while fractional ownership offers the potential for customisation and higher returns.
Here’s a table highlighting the key differences between REIT vs Fractional Ownership:
| Key Differences | REITs | Fractional Ownership |
| Ownership Structure | Shareholders own shares of the REIT | Investors directly own a fraction of the property |
| Control and Decision-Making | Limited control and voting rights over property decisions | Direct control and decision-making regarding the property |
| Investment Size and Entry Requirements | Low investment minimums, accessible to small investors | Higher investment minimums, usually higher minimum investment amounts. |
| Risk and Returns | Moderate risk and potential for stable returns | Higher risk due to direct ownership, potential for higher returns but also higher risk. |
| Liquidity and Marketability | High liquidity, shares can be bought or sold on exchanges | Low liquidity, selling the fractional ownership may be more challenging |
Which one to Choose Between REITs and Fractional Ownership
When choosing between REIT vs Fractional Ownership, examine your investment goals, risk tolerance, and preferences. While both options have their advantages, REITs tend to offer certain benefits that make them a compelling choice for many investors.
Firstly, REITs provide a higher level of diversification compared to fractional ownership. REITs give investors access to diverse real estate assets across sectors and geographies. This diversification helps mitigate risk by spreading investments across multiple properties.
Secondly, REITs offer liquidity and marketability. Their shares are traded on stock markets, making it easy for investors to buy or sell. This provides flexibility and the ability to exit or adjust positions in response to market conditions.
Finally, REITs also have expert management, which can benefit hands-off investors. Experienced real estate professionals handle property acquisition, management, and maintenance, relieving investors of the burden of day-to-day property responsibilities.
In navigating the comparison between REIT vs Fractional Investment, it’s important to understand the nuances of each. REITs, for instance, offer notable benefits such as diversification and liquidity.
On the other hand, fractional ownership also presents a unique set of advantages, the intricacies of which can be explored further in Fractional Property Ownership – Definition, Purpose, and Examples. The blog has complete overview including purpose, concept, and fractional ownership examples. This knowledge complements the decision-making process, aiding in the selection of a strategy that aligns best with your investment goals.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between REIT vs Fractional Ownership is crucial for investors seeking to diversify their portfolios with real estate. While REITs offer diversification and liquidity, fractional ownership provides direct control and the potential for higher returns. Consider investing goals, risk tolerance, and financial access while choosing between these possibilities.
Before investing, obtain professional counsel and research. For sustainable real estate investment options, explore platforms like SustVest, which offer environmentally and socially responsible opportunities.
Take charge of your investments and make informed choices with SustVest.

Founder of Sustvest
Hardik completed his B.Tech from BITS Pilani. Keeping the current global scenario, the growth of renewable energy in mind, and people looking for investment opportunities in mind he founded SustVest ( formerly, Solar Grid X ) in 2018. This venture led him to achieve the ‘Emerging Fintech Talent of the Year in MENA region ‘ in October 2019.




